Technology
TOCALO is a comprehensive manufacturer of surface treatments developing thermal spraying and other surface modification technologies.
We are a process manufacturer with world-class technological capabilities and achievements in the field of surface modification, particularly for our thermal spraying technology. Our thermal spraying technology and highly developed coating technology for producing chemical reactions and physical effects enable us to offer solutions for various customer needs.
Thermal spraying technology
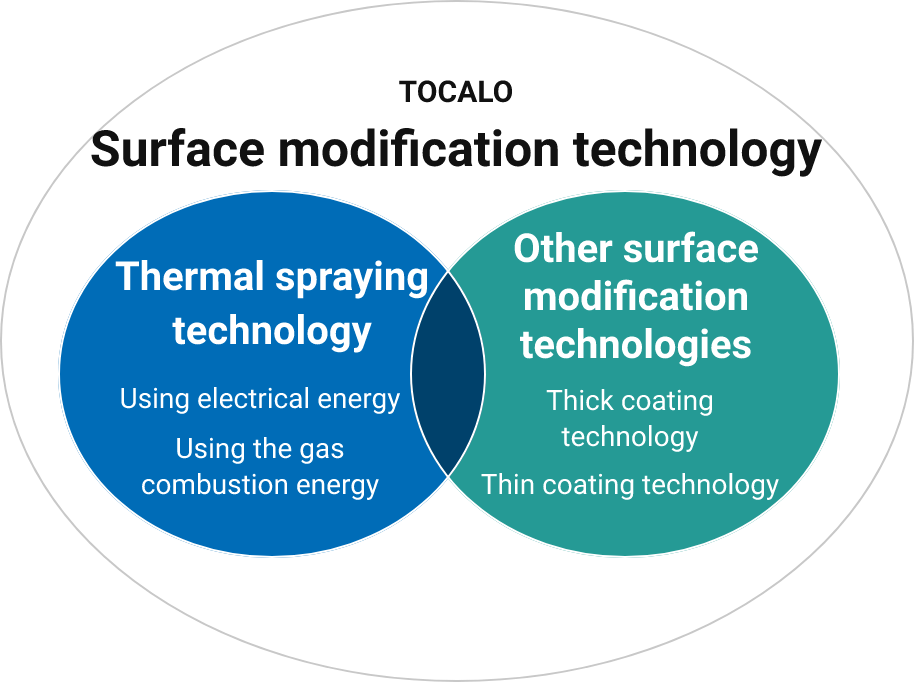
Atmospheric plasma spraying (APS)
Plasma is an electrically conductive gas containing electrically charged particles, ions and electrons.
A plasma jet is a high-temperature, high-velocity spray of gases compressed into plasma. Plasma spraying is a thermal spraying method in which extremely high energy density plasma heated to 10,000°C is used to melt powder materials of metal, alloys, and high melting-point materials, such as ceramics and cermet, which is composed of ceramics and metal or metal alloys, for spraying onto the workpiece.
Plasma spraying conducted under regular air pressure is called atmospheric pressure spraying (APS) to distinguish it from vacuum plasma spraying. The APS process can be used with a wide range of ceramics with various properties and can accommodate diverse environments. We take advantage of its versatility to select the optimal coating material, compose the most effective coating, and conduct strict quality control. The term “plasma spraying” usually refers to the APS spraying method.
Features
- Wide palate thermal spraying material options.
- Suitable for ceramics and other materials with high melting points.
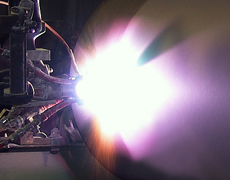
Vacuum plasma spraying
Vacuum plasma spraying (VPS) is carried out inside a vacuum chamber that is evacuated of oxygen and filled with an inert gas (argon) that is maintained at low pressure. VPS is essential to producing high-function coatings for various advanced technologies.

Features
- Coatings preserve the specifically designed characteristics of the coating materials.
- Activated metals, such as titanium, can be used for the coating.
- As the spraying speed of molten particles is faster than in oxygen, coatings with higher bonding strength and density can be used.
Arc spraying
Arc spraying uses a direct-current short-circuit electric arc to melt two wires of the coating material at the nozzle of spraying gun. The material droplets are then atomized and sprayed onto the substrate with compressed air. Electric arc spraying and gas-flame spraying method are both called wire processes. All metals and alloys in wire form are possible for arc spraying material.

Features
- Quick coating formation, ideal for objects with large processing areas.
- Greater adhesion and bonding strength than flame spraying.
- Capable of thicker coatings.
High velocity oxy-fuel spraying
High velocity oxy-fuel (HVOF) spraying uses increased pressure in the spraying gun combustion chamber to generate a high-speed flame comparable to a detonative combustion flame. Powder materials are fed in and melted or half-melted in the flame jet stream, then accelerated and sprayed at supersonic speed.
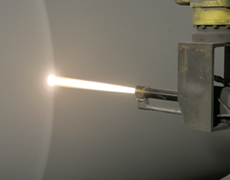
Features
- Extremely high density coatings with strong adhesion possible.
- Particularly suitable for wear-resistant coatings made of carbide cermet materials.
- Flame has less air content, inhibiting object oxidation.
Powder flame spraying
Powder flame spraying uses self-flux alloys in powder form for spraying materials, and oxygen or acetylene as a heat source. After the sprayed coating reaches the desired thickness, a fusing treatment is applied to cover open pores and form an alloy layer with the substrate, which provides high adhesiveness comparable to welding. In the fusing and solidifying process, the coating deposits a solid layer of boride and carbide, which adds exceptional wear resistance to the coating.
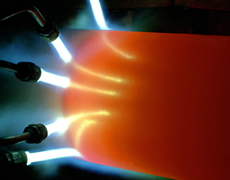
Features
- Produces a dense coating with almost zero porosity.
- Metallurgical bonding with the substrate creates high adhesion.
- Excellent resistance to corrosion, wear, and cavitation erosion, and high-temperature hardness.
Wire flame spraying
Wire flame spraying uses metals and alloys in wire form as spraying materials, and a combustion flame or electric arc as its heat source. The coatings are formed by spraying the molten materials onto the surface of the workpiece.
All metals and alloys in wire form are usable, such as copper, bronze, stainless steel, high carbon steel, molybdenum, and low melting point metals like aluminum and zinc.

Features
- Accommodates a wide range of coating thicknesses.
- Creates a moderate porosity coating, enabling oil retainment (improving lubricity).
- Minimal thermal impact on the substrate.
Suspension plasma spraying (SPS)
Suspension plasma spraying is a new plasma spraying method that delivers the coating material in a liquid suspension state, making it possible to spray fine particle powder material. Adjusting the thermal spraying conditions of the ultra-fine powder makes it possible to produce coatings with attributes for specific conditions, such as an ultra-dense, low-porous coating for enhance wear resistance or an ultra-porous coating with low thermal conductivity and catalytic support.
Features
- Able to form coatings with structures suited to the usage environment (ultra-dense, porous, columnar structure)
- Produces a smooth surfaced coating.
Other surface modification technologies
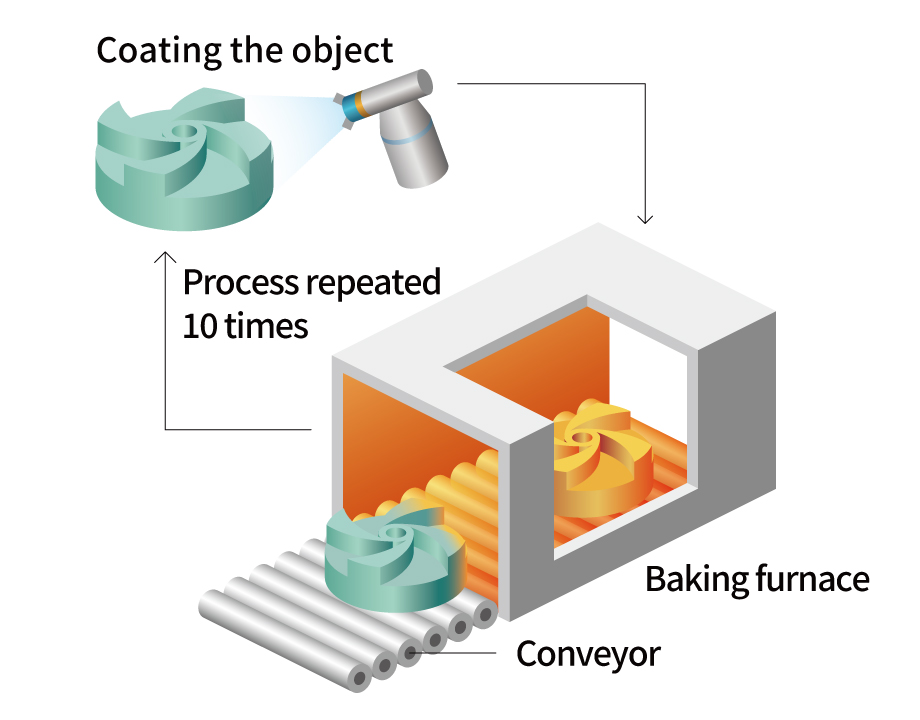
CDC-ZAC coating
CDC-ZAC coating is a chemical densification process that uses a chemical reaction to form a composite ceramic coating whose main component is chromium oxide (Cr2O3). The process is able to form coatings on complex shapes that are difficult with thermal spraying, and is extremely effective for machine parts that require wear and corrosion resistance.
Features
- High hardness(HV1000~2000)
- Wear resistance
- Corrosion resistance (high corrosion resistance against seawater, bases, and most acids and solvents)
- Low friction
- Adhesion resistance (molten metal, molten resin)
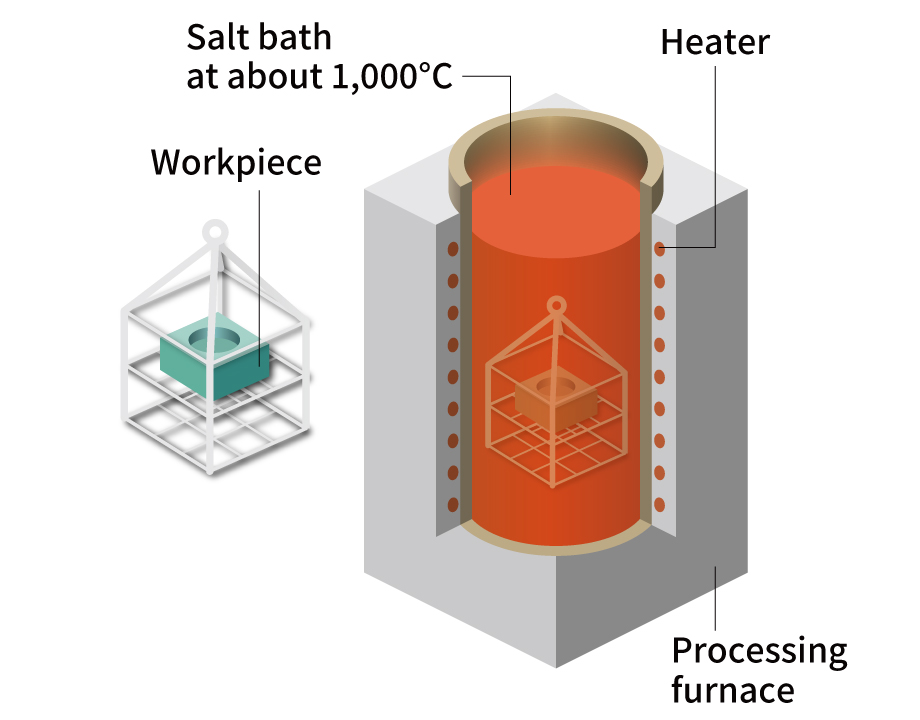
TD process
The TD process produces a high-function coating formed from carbide including niobium and chromium. In the process, the workpiece is uniformly coated by dipping it into the high-temperature salt bath. The coating is applicable to workpieces of complicated shapes and achieves high hardness. The TD process is a vital technology that is highly regarded in the mold production industry.
Features
- Wear resistance
- Anti-seizure
- High hardness
- Even complex shapes can be processed
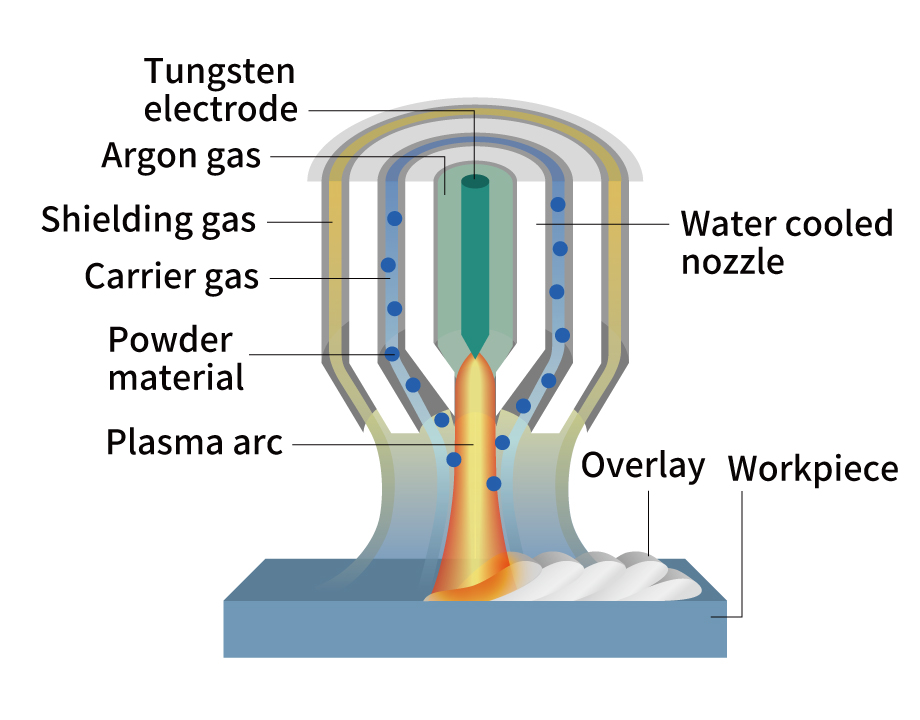
PTA process
Plasma transferred arc (PTA) is a surface overlay welding method using a high-energy plasma transfer arc. PTA does use powder instead of wire or rods for the overlay material, making it possible to process ceramics and other super hard materials.
PTA also accommodates compound and controlled ratios of metal alloy and ceramic powders, making it possible to form coatings with the optimal adhesiveness and amenable to finishing with a cermet coating after the overlay.
Features
- High adhesion (metallurgically bonded to substrate)
- Easily accommodates thicker coatings
- High thermal and abrasion resistance
- Anti-seizure
- Corrosion resistance
Wet coating
Wet coating is a technique for creating a thin coating by uniformly applying to the base material a liquefied material, which is then dried and cured. This technique allows selection of the most suitable coating performance for specific applications, including coatings that control surface free energy, such as water or oil repellency or hydrophilicity, and environmental barrier properties.
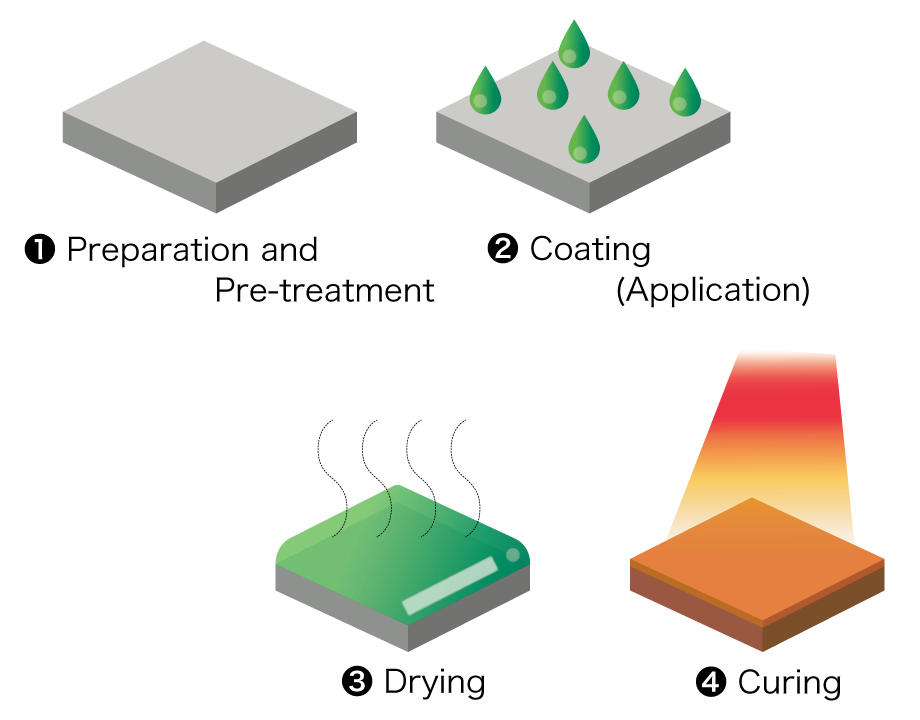
Features
- Low temperature processing possible (100°C or lower)
- Accommodates complex shapes (e.g., inner surface of small-diameter piping)
- Thin coating (down to micrometers)
Plasma surface treatment technology
Physical vapor deposition (PVD) processes use a physical reaction to form a thin coating on an object. TOCALO uses the arc ion plating PVD process, which offers superb adhesion properties for complex-shaped workpieces. This technique allows the selection of the optimal process for the workpiece material to minimize potential deformation caused by heat.
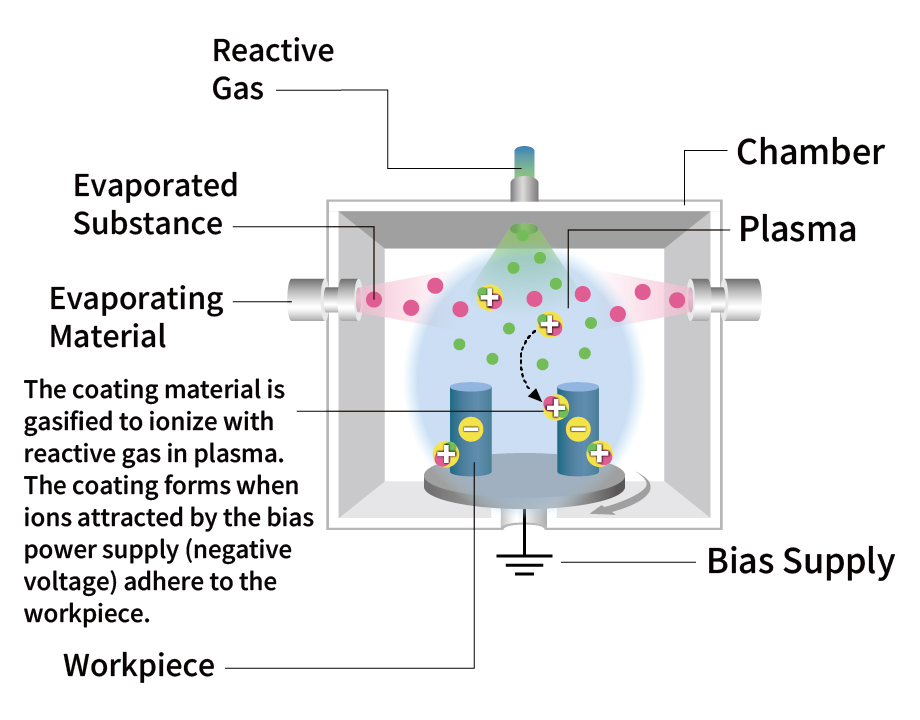
Features
- Low temperature treatment (250-550°C)
- Excellent adhesion
- Produces a dense coating
- Accommodates composite and multilayer coatings
Laser cladding process (TOCALO Laser Clad)
TOCALO Laser Clad (TLC) is an overlay technology that forms an overlay layer by injecting a powdered material and uses a laser beam as a heat source to melt and bond the material to the base material surface. The low heat input and thermal distortion enable workpiece overlay weld coating and repair that is problematic with conventional welding methods.
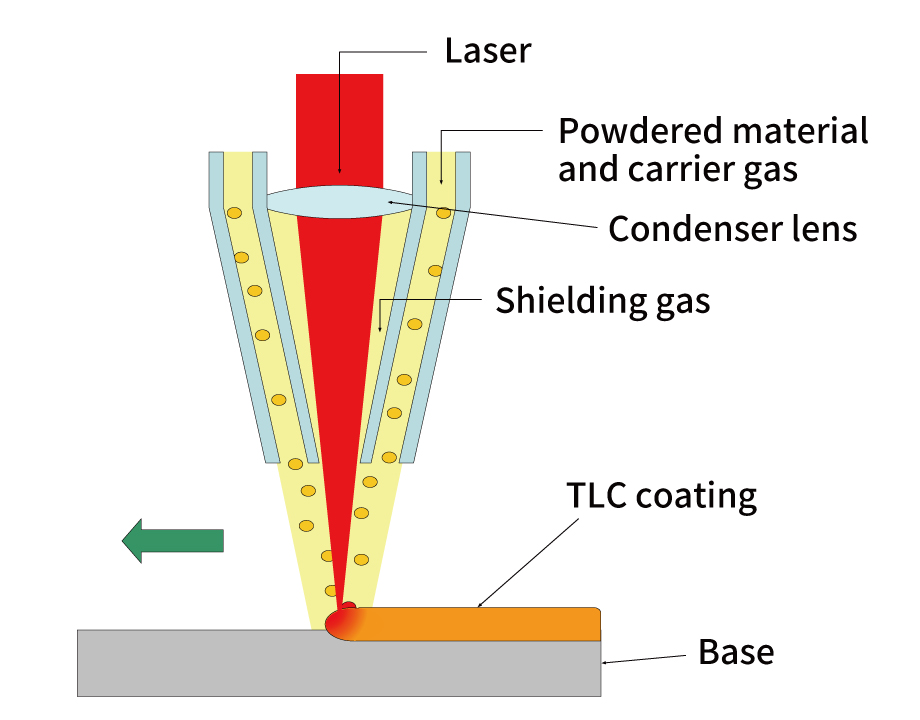
Features
- Low heat input to the base material
- Minimal thermal distortion and heat-affected zones
- Minimal base material dilution into the coating
- Easy control of coating thickness

